 Results
Results
The mean age of survivors and non-survivors was 72.9 ±9.3 years and 73.8 ±10.1 years, respectively; 48.2 percent of survivors and 62.5 percent of nonsurvivors were men (p<0.05).
Table 1 shows medical history and medication use. More survivors had been hospitalized before for treatment of pulmonary edema, and more survivors had a history of congestive heart failure. The prevalence of ischemic heart disease w as the same in both groups. Nonsurvivors more frequently used calcium channel blocker medication, and there was a tendency for more frequent use of p-blocker medication among nonsurvivors (p = 0.15).
Table 2 lists patient characteristics at the onset of mechanical ventilation. Nonsurvivors had a twofold increase in the incidence of myocardial infarction compared with survivors and a threefold increase in the frequency of anterior infarction. Nonsurvivors had a lower systolic blood pressure, respiratory rate, PaC02, and serum bicarbonate level, and a higher pH than did survivors.
By analysis of receiver operator characteristic curves, a blood pressure of 130 mm Hg had the best balance of sensitivity (84.4 percent) and specificity (82.1 percent) for mortality. Figure 1 shows that patients with myocardial infarction (open circles) had a lower initial systolic pressure than those patients without myocardial infarction, 128.8 ±48.8 mm Hg compared with 167.4 ±36.8 mm Hg (p<0.001).
Table 1—Medical History and Medication Use
| Survivors, % n = 56 | Nonsurvivors, % n = 32 | P | |
| Previous hospitalization for pulmonary edema | 35.7 | 12.5 | <0.025 |
| Congestive heart failure | 57.1 | 31.3 | <0.025 |
| Hypertension | 58.9 | 43.8 | NS |
| Angina | 42.9 | 40.6 | NS |
| Myocardial infarction | 51.8 | 46.9 | NS |
| Diabetes | 41.1 | 15.6 | <0.025 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 39.3 | 15.6 | <0.025 |
| p-blocker | 17.9 | 31.3 | NS |
| Ca+ * channel blocker | 23.2 | 43.8 | <0.05 |
| Digoxin | 53.6 | 50.0 | NS |
| Diuretic | 70.8 | 29.2 | <0.001 |
Table 2—Clinical Characteristics at Onset of Mechanical Ventilation
| Survivors, % n = 56 | Nonsurvivors, % n = 32 | P | |
| A. Discrete variables | |||
| MI at onset | 42.8 | 84.4 | <0.001 |
| Anterior MI | 19.6 | 59.4 | <0.001 |
| Inferior MI | 19.6 | 12.5 | NS |
| Cardiomegaly on CXR | 51.8 | 43.8 | NS |
| Pleural effusion on CXR | 23.2 | 25.0 | NS |
| Peripheral edema | 46.4 | 18.7 | <0.01 |
| Nonconscious | 37.5 | 34.4 | NS |
| Rales | 91.1 | 87.5 | NS |
| Cutaneous vasoconstriction | 76.8 | 78.1 | NS |
| B. Continuous variables | |||
| Heart rate | 109.7 ±27.4 | 109.2 ±25.7 | NS |
| Respiratory rate | 35.1 ±7.7 | 28.7 ±6.4 | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 166.1 ±41.9 | 108.2 ±.33.9 | <0.001 |
| Arterial pH | 7.17 ±.14 | 7.27 ±.15 | <0.005 |
| Arterial Pco2 | 65.6 ±20.7 | 46.7 ±16.5 | <0.001 |
| a/A ratio for oxygen | 0.29 ±.16 | 0.27 ±.17 | NS |
| HCO, | 23.2±4.7 | 20.2 ±4.6 | <0.005 |
| BUN | 29.3 ±13.7 | 30.6 ±13.6 | NS |
| HCT | 41.1 ±6.9 | 38.8±5.8 | NS |
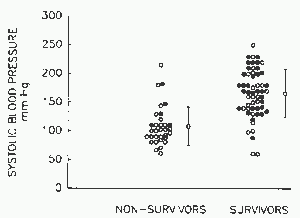
Figure 1. Systolic blood pressure at time of intubation for nonsurvivors and survivors. Open circles represent episodes associated with an acute myocardial infarction.
Category: Pulmonary disease
Tags: mechanical ventilation, myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema, systolic blood pressure
© 2011 - 2024 buy-asthma-inhalers-online.com. All rights reserved.